Description
Going forward, AI algorithms will be incorporated into more and more everyday applications. For example, we might want to include an image classifier in a smart phone app. To do this, we had to use a deep learning model trained on hundreds of thousands of images as part of the overall application architecture. A large part of software development in the future will be using these types of models as common parts of applications.
In this project, we'll train an image classifier to recognize different species of flowers. we can imagine using something like this in a phone app that tells us the name of the flower our camera is looking at. In practice we had train this classifier, then export it for use in our application. We'll be using this dataset from Oxford of 102 flower categories, you can see a few examples above.
Goal:
Using TensorFlow, train an image classifier that can recognize different species of flowers. Check My - Jupyter notebook.Dataset
We will use `tensorflow_datasets` to load the Oxford Flowers 102 dataset .The Oxford Flowers 102 dataset is a consistent of 102 flower categories commonly occurring in the United Kingdom. Each class consists of between 40 and 258 images. The images have large scale, pose and light variations. In addition, there are categories that have large variations within the category and several very similar categories.
Data Exploration
This dataset has 3 splits: train, test, and validation.
We'll also need to make sure the training data is normalized and resized to 224x224 pixels as required by the pre-trained networks. The validation and testing sets are used to measure the model's performance on data it hasn't seen yet, but we'll still need to normalize and resize the images to the appropriate size.
Shape and Corresponding Label

Build and Train the Classifier
Model.Summary()
Training and Validation Performance

Testing your Network
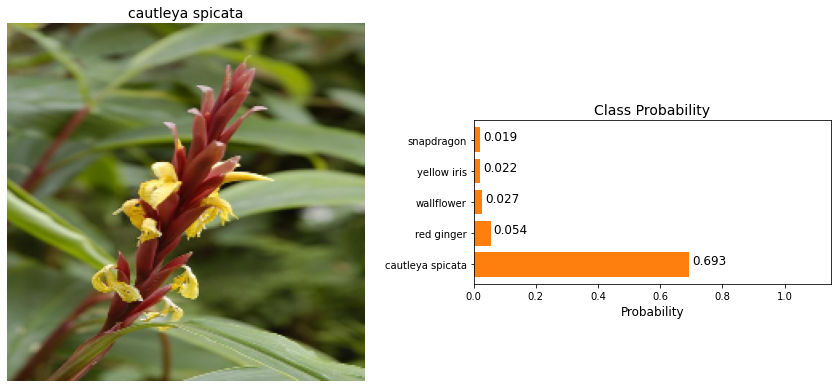
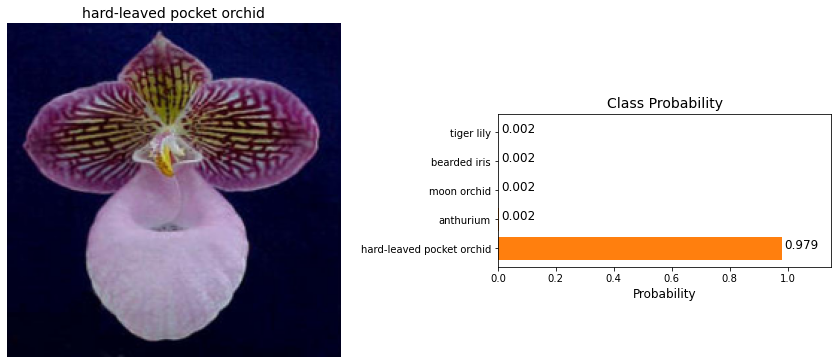
Final Output
It's always good to check the predictions made by your model to make sure they are correct.